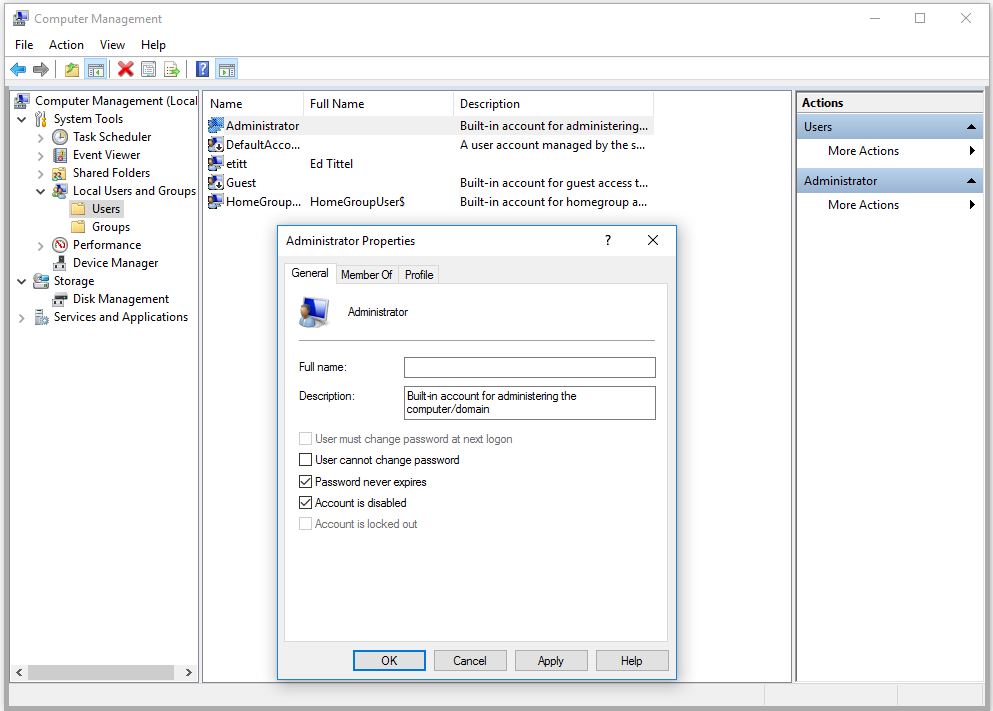
In today’s digital landscape, securing access to devices and corporate networks is more critical than ever. Microsoft offers two advanced authentication solutions: Windows Hello and Windows Hello for Business. While both provide passwordless sign-in options and enhanced security, they are designed for different users and use cases. Windows Hello is ideal for personal devices, offering quick and convenient biometric or PIN-based login. On the other hand, Windows Hello for Business is tailored for enterprise environments, integrating with corporate policies, Active Directory, and Azure AD to provide secure, scalable, and compliant authentication for organizations.
In this guide, we will explore the differences, benefits, and use cases of each solution, helping you decide which one best fits your personal or business security needs.
In today’s digital world, securing access to devices and corporate networks is more important than ever. Microsoft provides two advanced authentication solutions: Windows Hello and Windows Hello for Business. Both offer passwordless sign-in and enhanced security, but they serve different purposes and user types.
Windows Hello is ideal for personal devices, enabling quick login via PIN or biometrics. Windows Hello for Business, on the other hand, is designed for enterprise environments, integrating with Active Directory (AD) and Microsoft Entra ID for secure, scalable authentication.
This guide will break down the differences, benefits, and use cases for each solution, helping you determine which fits your personal or organizational needs.
What Is Windows Hello?
Windows Hello is a secure, built-in authentication method in Windows 10 and Windows 11. Unlike traditional passwords, it allows sign-in via PIN or biometric verification, with credentials bound directly to the device.
Key features:
- Biometric and PIN options: Users can choose facial recognition, fingerprint scanning, or PIN login.
- Device-bound credentials: Authentication data never leaves the device, reducing phishing risks.
- Enhanced security: Protects against spoofing and replay attacks.
Supported sign-in options:
- Facial Recognition – Uses a near-infrared camera compatible with the Windows Biometric Framework. Requires antispoofing and liveness detection to ensure high security.
- Fingerprint Recognition – Requires a supported fingerprint sensor. Security varies depending on sensor type.
- PIN – Works with the Trusted Platform Module (TPM) and can include letters, numbers, and special characters.
Tip: Learn more about setting up Windows Hello.
What Is Windows Hello for Business?
Windows Hello for Business (WHfB) extends Windows Hello with enterprise-grade security and management features, such as:
- Device attestation
- Conditional access policies
- Certificate-based authentication
- Multifactor authentication (MFA)
WHfB integrates with AD or Microsoft Entra ID, providing secure sign-in with a PIN or biometric gesture plus a device-specific credential.
Setup process includes five key phases:
- Device Registration – Registers the device with AD or Entra ID.
- Provisioning – Launches a Cloud Experience Host to create credentials and keys.
- Key Synchronization – Required for hybrid deployments to sync public keys.
- Certificate Enrollment – For certificate-based authentication.
- Authentication – Validates the user with the private key and biometric/PIN.
Reference: Microsoft provides a detailed WHfB guide here.
Windows Hello vs Windows Hello for Business
| Feature | Windows Hello | Windows Hello for Business |
|---|---|---|
| Target Users | Personal or small business users | Large organizations with centralized management |
| Authentication | PIN or biometrics tied to the device | Multi-phase FIDO2 authentication via AD or Entra ID |
| Security | TPM-backed key-based authentication | TPM + certificate-based, MFA, device attestation, conditional access |
| Management | Configured individually by end users | Managed centrally via MDM or Group Policy |
| Licensing | Included with Windows 10/11 | Requires Pro, Enterprise, or Education editions + AD/Entra ID registration |
Key Differences Explained
1. User Targeting
- Windows Hello is for individuals or small organizations, where users configure their own devices.
- Windows Hello for Business is for enterprises, requiring device registration and identity integration.
2. Authentication Method
- Windows Hello: FIDO2-based, device-bound PIN/biometric login.
- Windows Hello for Business: Multi-step authentication leveraging TPM, certificates, and MFA.
3. Security Features
- Windows Hello: Secures credentials locally, reduces phishing risks.
- WHfB: Supports advanced features like conditional access, device attestation, and certificate-based authentication.
4. Configuration
- Windows Hello: Set up via Settings → Accounts → Sign-in options.
- WHfB: Managed centrally with Intune, ManageEngine, or Group Policy. Admins can enforce PIN policies and biometric requirements.
5. Licensing
- Windows Hello: Free with Windows 10/11 editions. TPM recommended.
- WHfB: Requires Windows Pro/Education/Enterprise and AD/Entra ID registration; advanced management may incur extra costs.
Conclusion
Choosing between Windows Hello and Windows Hello for Business depends on your environment:
- Personal use: Windows Hello provides convenient, secure, device-bound authentication.
- Enterprise use: WHfB ensures centralized control, compliance, and robust security for large-scale deployments.
For a deeper dive into Windows security best practices, check out: