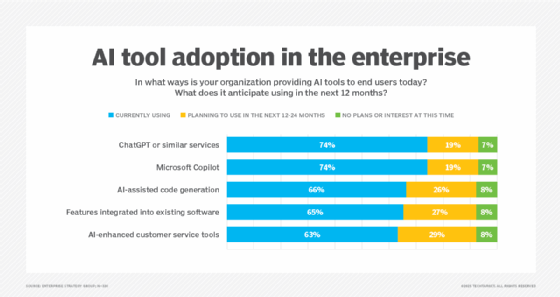
Generative AI has made it possible for end users to write functional code quickly. However, IT teams must remain vigilant to ensure that AI-assisted code does not compromise security, efficiency, or organizational compliance. This process is often referred to as vibe coding, a term describing the casual use of AI to develop scripts, tools, or applications.
📌 What is Vibe Coding?
Vibe coding allows anyone—technical or non-technical—to conceptualize and generate code using AI tools like GitHub Copilot, ChatGPT, or Claude. While it can accelerate prototyping and hobby projects, IT administrators should understand the implications of end-user AI coding in enterprise environments.
Reference: Omdia Enterprise Strategy Group
🖥️ Examples of Vibe Coding in Practice
AI-assisted coding can create useful tools quickly:
- Obsidian plugins for custom note-taking workflows.
- Python scripts for automation, such as controlling devices or processing media files.
- AutoHotKey utilities to replicate desktop app behaviors.
- RadioSHIFT or other experimental projects using AI-generated code.
These examples illustrate that end users can generate working, functional code within minutes, sometimes outperforming the time it would take manually.
Reference: GitHub Copilot
⚠️ AI-Written Code: Functional but Not Always Efficient
AI-generated code may work, but it often suffers from inefficiencies:
- Code may run repeatedly on unnecessary loops or checks.
- Inefficient operations can multiply across users, affecting infrastructure performance.
- AI might implement generic solutions without optimizing for the specific environment.
For instance, a plugin scanning an entire document repeatedly instead of focusing on relevant characters can cause thousands of unnecessary operations.
Reference: Microsoft Docs – AI-Assisted Development
🔐 Security Risks of AI-Generated Code
AI-written code may not follow secure coding practices:
- Minimal attention to race conditions or secure data handling.
- Possible inclusion of malicious or unsafe instructions from unvetted AI tools.
- End users may unintentionally expose organizational systems to vulnerabilities.
This makes oversight essential, even for seemingly benign AI scripts.
Reference: NIST – AI Risk Management Framework
👁️ Oversight and Governance Are Key
Vibe coding requires management oversight:
- IT teams should track which AI tools employees are using.
- Policies should define approved vs. unapproved AI tools.
- Developers or IT admins may need to review AI-generated code before deployment.
Recent research shows that over half of knowledge workers use AI tools for work without official approval, increasing potential risk.
Reference: Enterprise Strategy Group Research
⚖️ Balancing Innovation and Risk
Organizations should encourage responsible AI experimentation while mitigating risks:
- Identify user-driven AI coding through monitoring and reporting.
- Define governance policies for AI-assisted development.
- Train users on secure and efficient coding practices.
- Leverage internal review processes before deploying AI-generated tools in production.
This approach allows end users to benefit from AI productivity gains without compromising enterprise security or efficiency.
🔗 Further Reading and Resources
- GitHub Copilot Overview – AI-assisted coding for developers.
- Microsoft AI Services – Microsoft AI tools and APIs.
- NIST AI Risk Management Framework – Guidelines for AI security and risk mitigation.
- Enterprise Strategy Group – Research and insights on end-user computing and AI adoption.