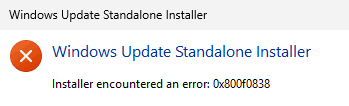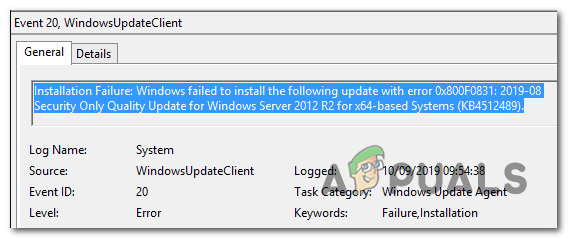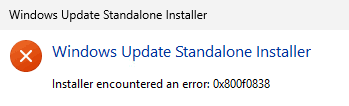
Error 0x800f0838 is a common issue that occurs during the installation of Windows updates, particularly when using .MSU (Microsoft Standalone Update) files. This error interrupts the installation process, rolls back any partially applied changes, and displays a failure message along with the error code. The underlying cause is often the absence of checkpoint updates, a feature introduced in Windows 11 24H2 to reduce the size of monthly updates.
Error 0x800f0838 often occurs during Windows update installations, particularly when using offline update methods like manual installations or third-party patch management tools. This error can be triggered if checkpoint updates, a feature introduced in Windows 11 24H2, are missing or not properly installed. These updates are essential for streamlining the update process, and their absence can result in the failure to apply subsequent updates.
In addition to missing checkpoint updates, other common causes for this error include:
- Corrupted Windows system files
- Malfunctioning Windows Update services
- Damaged update cache files
To resolve this issue, make sure all prerequisite updates, including checkpoint updates, are installed first. If you’re using offline update methods, ensure that all update dependencies are resolved manually. For more troubleshooting steps and detailed guidance, refer to the Microsoft Support page.
Proven Fixes for Error 0x800f0838
Below, we’ll walk you through effective solutions to fix this error and restore proper update functionality.
Important Note: Before you begin, ensure that you back up your data and have at least 20GB of free space on your system drive (C:). Low disk space can cause update failures, so it’s crucial to make space before proceeding.
1. Run SFC and DISM Scan
Running SFC (System File Checker) and DISM (Deployment Image Servicing and Management) scans can repair corrupted system files and restore a healthy Windows image. These tools address common causes of update failures by repairing essential components.
- Open the Windows Start menu.
- Search for “Command Prompt” and run it as an administrator.
- In the Command Prompt, enter the following command:
sfc /scannow
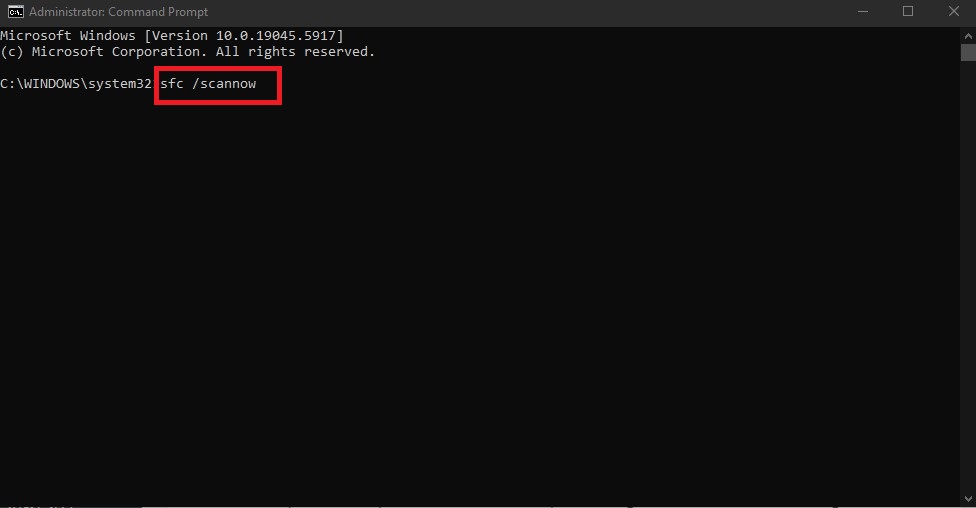
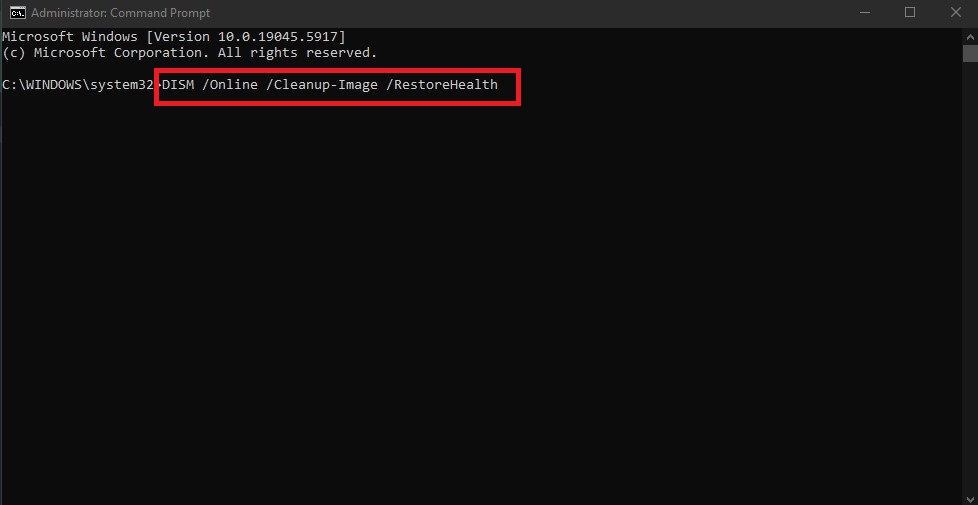
- Once complete, keep the Command Prompt open and run:
DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth
- After both scans finish, retry the Windows Update process.
2. Reset Windows Update Components
Resetting Windows Update components clears corrupted temporary files and resets related services. This gives the update process a clean state and resolves errors caused by file conflicts or partial update attempts.
- Open the Windows Start menu.

- Search for “Command Prompt” and run it as an administrator.
- Execute the following commands one by one:
net stop wuauserv
net stop bits
net stop cryptsvc
ren C:\Windows\SoftwareDistribution SoftwareDistribution.old
ren C:\Windows\System32\catroot2 Catroot2.old
net start wuauserv
net start bits
net start cryptsvc
3. Manually Install Updates
Installing updates manually through PowerShell or Command Prompt allows you to bypass broken update mechanisms. Begin by installing the SSU (Servicing Stack Update) to ensure compatibility, followed by the main update (e.g., KB5050009). This method is useful when Windows Update fails due to service errors or corruption.
- Open your preferred browser.
- Go to https://www.catalog.update.microsoft.com
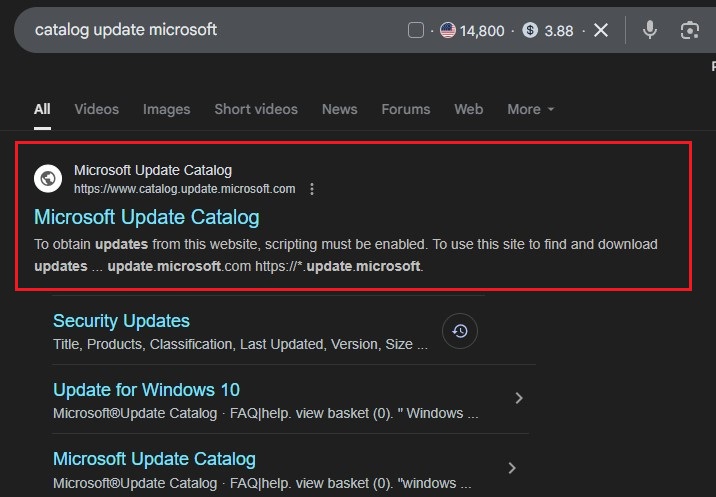
- Search for:
Latest SSU (e.g., "KB5043080") Your target update (e.g., "KB5050009")
- Download the “Windows 11” and “x64” .msu files.
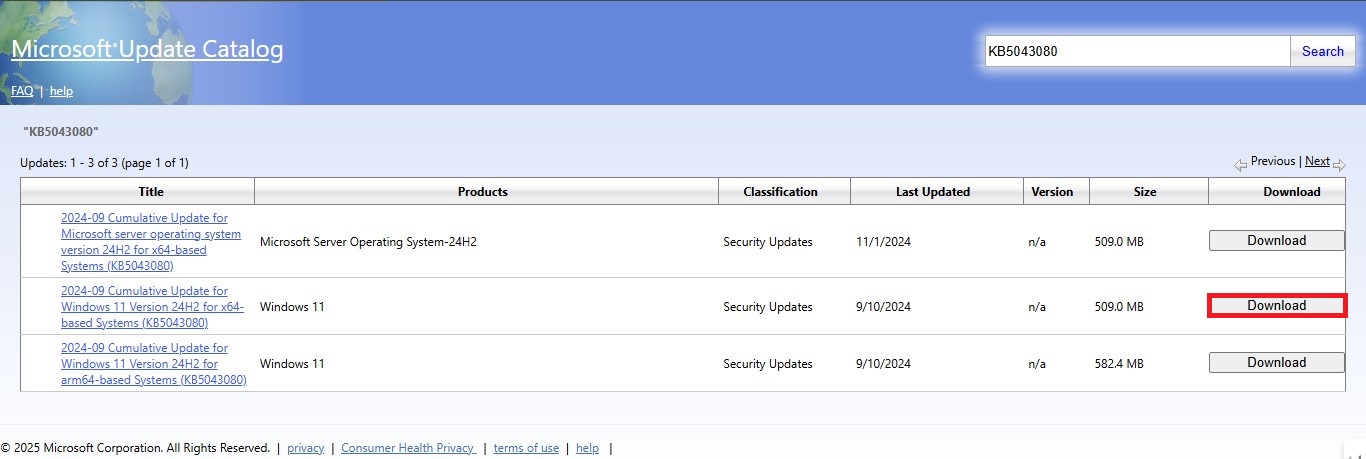
- Create a folder in C: (e.g., C:\Updates) and move both files there.
- Open Command Prompt or PowerShell as Administrator.
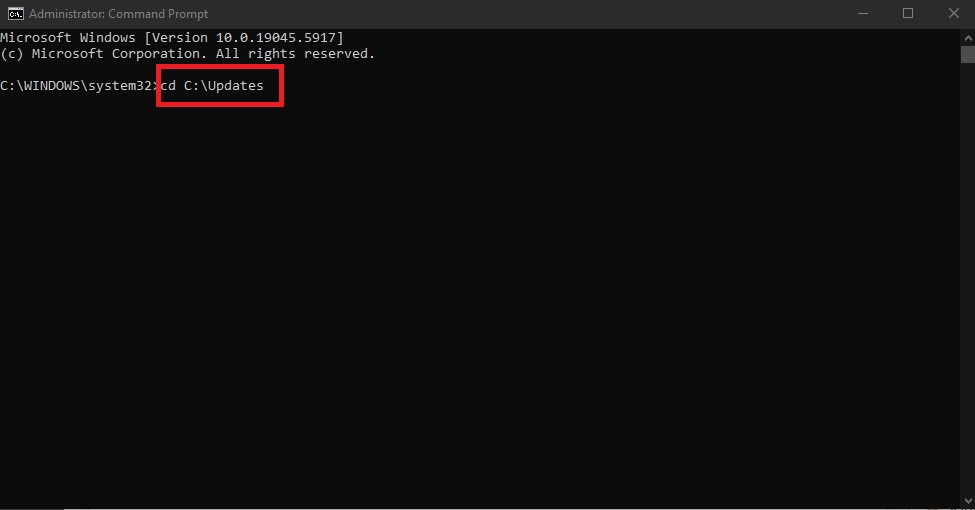
- Navigate to your update folder:
cd C:\Updates
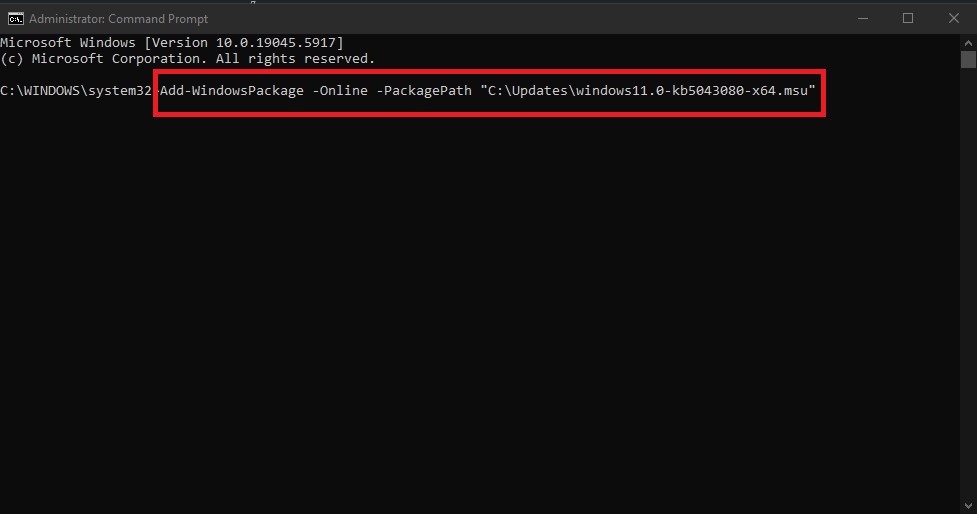
- Run the SSU installer (adjust filename if needed):
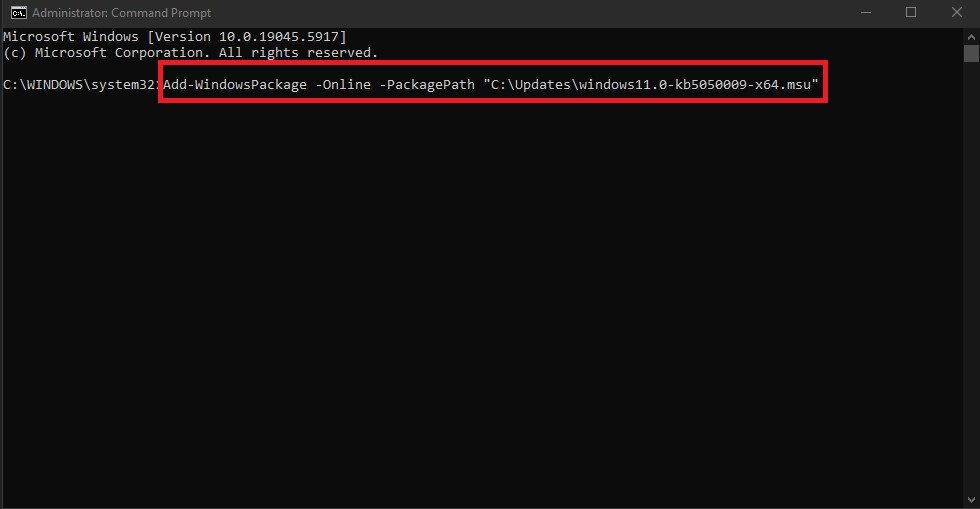
Add-WindowsPackage -Online -PackagePath "C:\Updates\windows11.0-kb5043080-x64.msu"
Wait for the process to complete.
- Then, install the Main Update:
Add-WindowsPackage -Online -PackagePath "C:\Updates\windows11.0-kb5050009-x64.msu"
- Restart your PC after installation completes.